If you want to learn Android programming there are a lot of Android tutorials and other learning materials online. There are lots of beginner tutorials and tons of advanced tutorials from various sources. We at SitePoint also offer a new Android development tutorial every now and then.
When there is so much information and you are a beginner, it’s easy to get confused about where to start. To make it easy for you and with no illusions that this list of Android tutorials is the best or complete, here are 12 Android tutorials to start with.
Not all the tutorials and their content are strictly beginner beginner focussed. Some of them start out for beginners and then delve into more advanced topics. So if you can’t follow everything in every single tutorial, don’t get desperate or frustrated.
If you encounter a hurdle, just spend more time with the tutorial, reading it a couple of times if necessary. If you are still not on friendly terms with it, there is no drama – just move forward and revisit it later.
Building Your First App
Naturally, we start the list with a tutorial from Google, the creators of Android. The ‘Building Your First App‘ tutorial starts from the very beginning and it’s suitable for absolute beginners. If you have no programming knowledge whatsoever, don’t expect to be able to handle the tutorial but if you have some programming background, it’s easy.
The tutorial has several ‘Best Practice’ sections at the end. This is good because all the important content about the topic in one place and you just have to read it.
Android Development – Tutorial
The reason this tutorial is near the top is that it’s very up-to-date (based on Android 4.4, the latest Android version as of today).
This tutorial has more topics and information than the tutorial from Google, so if you are looking for an in-depth tutorial, this is one the.
It’s not an easy or quick tutorial. If you want to get the most from it, you will need quite a lot of time to read it from start to finish. It can be a great source if you need to consult a given topic in detail.
3. Video Tutorials Series
I find video tutorials less useful (except when they teach design, animation, or any other visual topic) but for many people they are the preferred way of learning. If you belong to this group, you will love this series of video tutorials.
It’s a comprehensive series of video tutorials ranging from under 5 to 15 minutes in length. Similarly to the previous two tutorials, this series covers everything from absolute beginner level to advanced topics.
An Android Tutorial/Book
It might be old-school, but for me the best way to get a complete idea about something is by reading a book about it. In a book, everything is organized logically, pages are numbered and keep their layout and there is enough text to explain the and code/graphics. The first two tutorials in this list are book-like but if you want something more authentic you could print them. Even better, a pdf tutorial, like this one, is a much better option.
This is one more general tutorial that covers Android development from beginner level to advanced.
Game Development Series
If you have some knowledge about Android but you want to delve into games development, this series of video tutorials is a great start. The series starts with the very basics of Android (and Eclipse) but my personal feeling is that if you are a total stranger to Android, the journey will be too hard.
From what I saw, the series mentions general Android as well, not only game development. If you don’t know Android basics, my advice is to first read some of the general Android tutorials and then move to specialized topics, such as game development.
Better User Interfaces with the Android Action Bar
After you have had enough of general Android tutorials, let’s move to tutorials for common tasks. For some of these topics you can find information in the general tutorials as well but if you want more detail, this is for you. The first tutorial is about how to build Better User Interfaces with the Android Action Bar.
In this tutorial you will learn how to set up the action bar, how to add actions, how to split, hide, and overlay it, as well as how to add navigation. You will also learn about action bar interactivity, such as how to handle clicks on its items and to use action views.
Learning to Parse XML Data in Your Android App
While you could write Android applications that do not involve any data input, often you will need external data. In such cases you need to know how to handle this data. XML can help you a lot and this is why I’ve included a tutorial on how to Parse XML Data in Your Android App.
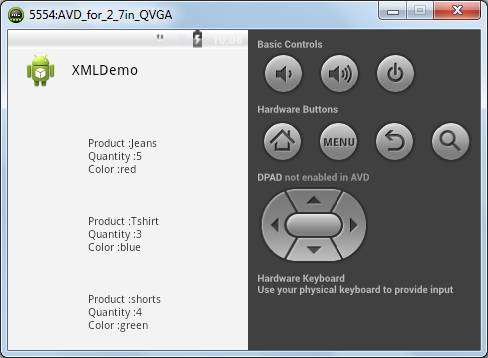
This tutorial leads you step by step in the world of XML parsing. It also helps you create a parser that will look like the one shown in the next screenshot.
Some More Online Web Sites Are..
- www.javatpoint.com/android-tutorial
- developer.android.com/
- www.tutorialspoint.com/android/
- www.codelearn.org/android-tutorial
- www.vogella.com/tutorials/Android/article.html
- developer.android.com/
- www.tutorialspoint.com/android/
- www.javatpoint.com/android-tutorial
- www.codelearn.org/android-tutorial
- www.vogella.com/tutorials/Android/article.html
- www.raywenderlich.com/78574/android-tutorial-for-beginners-part-1
- www.coreservlets.com/android-tutorial/
- www.mkyong.com/tutorials/android-tutorial/
- www.sitepoint.com/12-android-tutorials-beginners/ programmerguru.com/android-tutorial/ www.edumobile.org/tutorials/android/
- www.androidhive.info/